
V E R B S N O U N S P R E P O S I T I O N S: V E R B S: Practice Latin Verb Tenses as J i g s a w P u z z le s: ESSE (“to be”) in the Present and Imperfect
Latin grammar has retained many features of Proto-Indo-European, particularly in its noun declensions. Nouns, pronouns, adjectives Nominal inflections are fusional, i
How to Learn to Speak Latin. Latin may be known as a “dead language” but it can still be learned and spoken today. Not only will you be enhancing your linguistic
Study cases and declensions. The case gives a noun its distinct “role,” essentially dictating to the reader/listener how that noun functions within the sentence. The
Declining Latin nouns is a matter of memorizing the different forms of the five declensions. The nominative case is normally used for the subject of a sentence while
NEXT: Latin words change endings according to their duty. ACTORS have a basic spelling.”Marcus Brutus”. ACTEEs change that spelling to end in the -m sound [-am




Latin (Latin: lingua latīna, IPA: [ˈlɪŋɡʷa laˈtiːna]) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages.

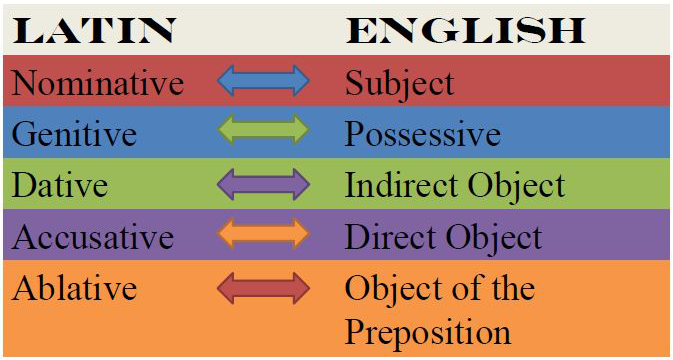

Latin has almost the same inflection structure as Ancient Greek. It uses a different alphabet, though. Latin has seven different noun cases: nominative, vocative,
Just to make things more complicated, certain masculine nouns are “weak” and take an “n” ending in all cases except the nominative. For example, most of the
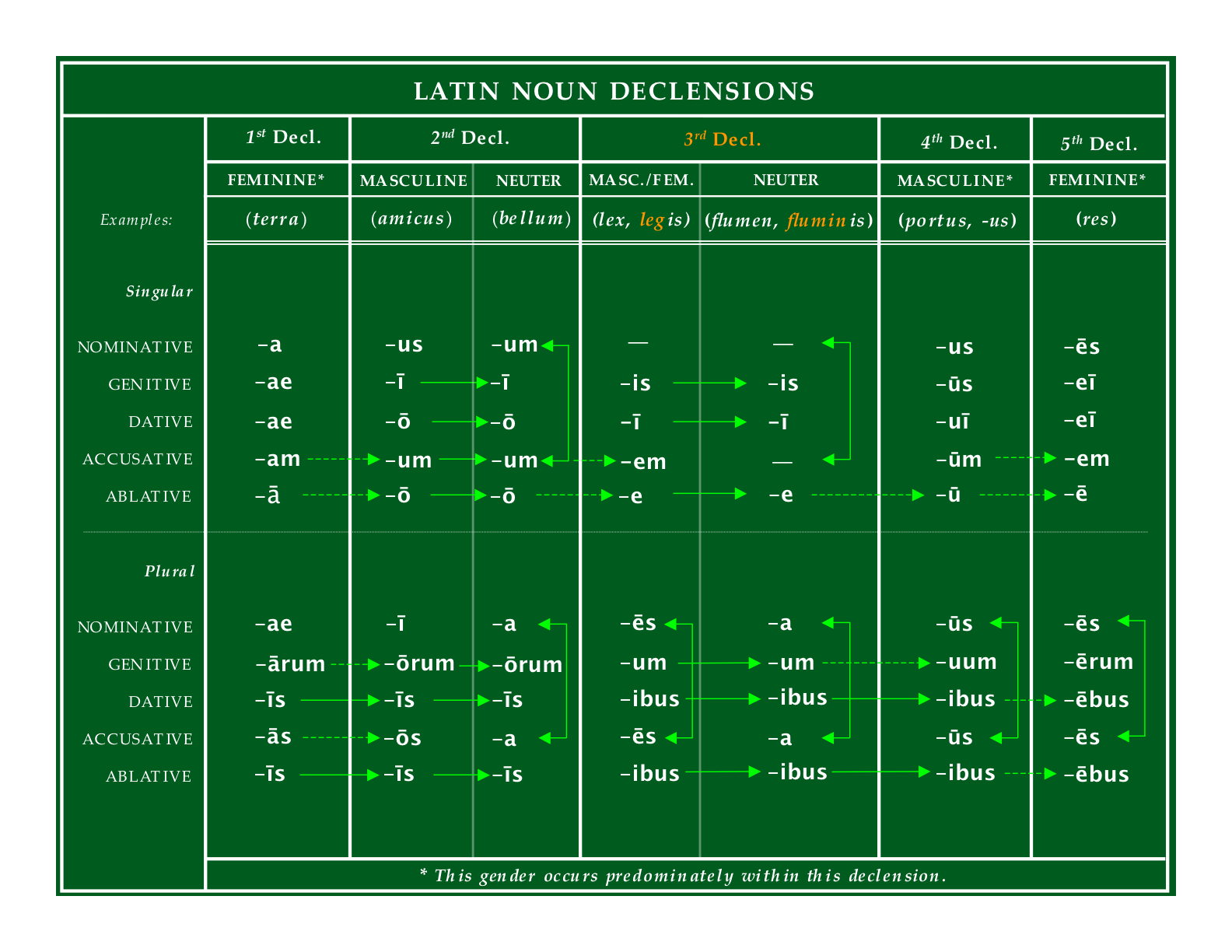
An example of a Latin noun declension is given below, using the word homo (man, human), which belongs to Latin’s third declension. homo (nominative and vocative
